HORIZONTAL TAIL SIZING GRAPH
This screen is used to determine the horizontal tail size for adequate static stability for conventionally configured aircraft.
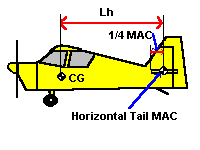
{bml bm86.BMP}The value Lh is the distance from the quarter chord of the horizontal tail Mean Aerodynamic Chord (MAC) to the centre of gravity of the aircraft. The value Vh is the tail volume coefficient. The higher this value is , the higher the degree of pitch stability. Typical light aircraft have a value of 0.5. The practical range is between 0.3 and 0.6. The value MAC is the mean aerodynamic chord of the wing.
The Y axis of the graph is the required horizontal tail area. The X axis of the graph is the ratio of the Lh and the wing MAC. The higher this ratio the less horizontal tail area is required for a given horizontal tail volume coefficient ie; a horizontal tail along way from the centre of gravity of the aircraft has more effect than a similar sized tail closer to the centre of gravity.
Values may be read off the graph by clicking anywhere within the boundaries of the graph.
Repeatedly clicking on one spot will cause the value for the tail area to be shown for each of the tail volume coefficients plotted.
The diagram below shows the relationship of the dimensions.
The selection of a suitable tail area would be performed as follows;
1.Select a suitable Vh value eg; 0.4
2. Determine the distance between the tail quarter chord of the tail Mean Aerodynamic Chord (MAC) and the aircraft Centre of Gravity.
3. Click on the graph at the value for the Lh/MAC. Continue to click until the value for a
Vh equal to 0.4 is obtained.
Alternatively, print out the graph and interpolate for the Lh/MAC and Vh equal to 0.4.
To print the graph;
Click on the PRINT button.
To save the graph as a bitmap picture file;
Click on the SAVE button.
To exit this screen;
Click on the CLOSE button